Friday, December 29, 2023
Morphology and Behavior of Fleas
Monday, December 25, 2023
Merry Christmas
Saturday, December 23, 2023
Why the Victims of a Praying Mantis Don't Have a Prayer 🐛 Into The Wild ...
Wednesday, December 20, 2023
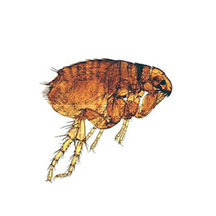
Flea
Sunday, December 17, 2023
How Paper Wasps ‘Tap’ to Select the Identity of their Larvae 🪰 Into The ...
Thursday, December 14, 2023
Glow Worms Trap Insects With Bioluminescent 'Fishing Lines'🪱 Into The Wi...
Monday, December 11, 2023
Earwigs
Earwigs make up the insect order Dermaptera. With about 2,000 species in 12 families, they are one of the smaller insect orders. Earwigs have characteristic cerci, a pair of forcep-like pincers on their abdomen, and membranous wings folded underneath short, rarely used forewings, hence the scientific order name, "skin wings". Some groups are tiny parasites on mammals and lack the typical pincers. Earwigs are found on all continents except Antarctica.
Earwigs are mostly nocturnal and often hide in small, moist crevices during the day, and are active at night, feeding on a wide variety of insects and plants. Damage to foliage, flowers, and various crops is commonly blamed on earwigs, especially the common earwig Forficula auricularia.
Earwigs have five molts in the year before they become adults. Many earwig species display maternal care, which is uncommon among insects. Female earwigs may care for their eggs, and even after they have hatched as nymphs will continue to watch over offspring until their second molt. As the nymphs molt, sexual dimorphism such as differences in pincer shapes begins to show.
Some earwig specimen fossils are in the extinct suborders Archidermaptera or Eodermaptera, the former dating to the Late Triassic and the latter to the Middle Jurassic. Dermaptera belongs to the major grouping Polyneoptera, their closest living relatives being the angel insects of the order Zoraptera.
Read more, here.
Friday, December 8, 2023
Carpenter Beetle
Tuesday, December 5, 2023
Born Pregnant: Aphids Invade with an Onslaught of Clones | Deep Look
Saturday, December 2, 2023
Carpenter Ants
Carpenter ants (Camponotus spp.) are large (0.3 to 1 in or 8 to 25 mm) ants indigenous to many forested parts of the world.
They build nests inside wood consisting of galleries chewed out with their mandibles, preferably in dead, damp wood. However, unlike termites, they do not consume wood, discarding a material that resembles sawdust. Sometimes, carpenter ants hollow out sections of trees. They also commonly infest wooden buildings and structures, and are a widespread nuisance and major cause of structural damage. Nevertheless, their ability to excavate wood helps in forest decomposition. The genus includes over 1,000 species. They also farm aphids. In the farming, the ants protect the aphids while they excrete a sugary fluid called honeydew, which the ants get by stroking the aphids with their antennae.
Read more, here.